Antoine, Flo, and Enora were in Geneva last week and reported that artificial intelligence was the main talking point at the Swiss IT forums. While most of us have interacted with tools like ChatGPT in our personal lives, the real question remains: Are businesses truly integrating AI and large language models (LLMs) into their daily operations? The short answer is yes—but it’s still a work in progress. Companies are gradually moving beyond AI experimentation and exploring how these powerful tools can reshape their workflows, boost productivity, and transform their business models. So, what’s the state of AI today, and how does this rapid evolution impact IT infrastructure? Let’s dive into where things stand.
Riding the AI hype cycle
To understand AI’s trajectory, it’s helpful to refer to Gartner’s Hype Cycle model, which outlines the stages that emerging technologies undergo. Right now, AI is in the spotlight, especially generative AI tools like ChatGPT, Gemini, and Claude. These technologies are at the “Peak of Inflated Expectations,” where businesses are excited about the potential but still exploring the practicalities.
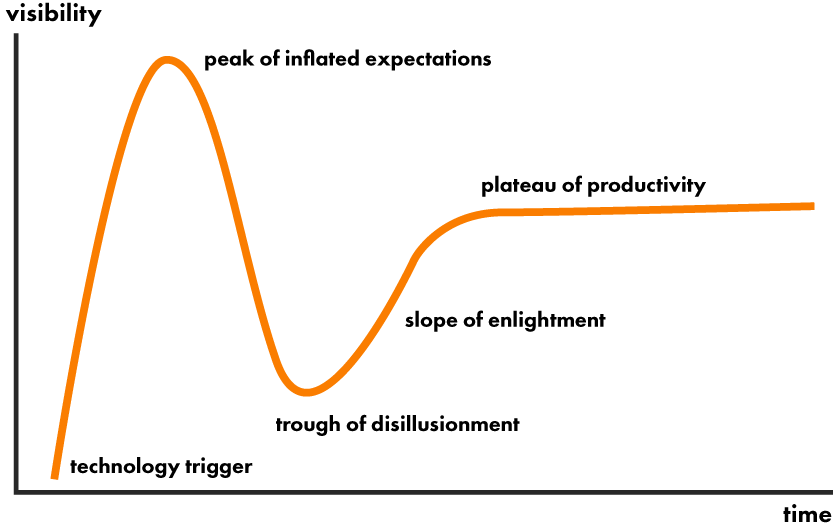
Source: Wikipedia
Generative AI in 2024 is living up to much of the hype, but as seen with many technologies, it also faces challenges. According to Gartner, while AI experimentation is at an all-time high, most businesses are still in the discovery phase, learning how to scale these solutions for broader business impact. Companies are starting to realize that adopting AI is not as straightforward as initially thought and that scaling AI within their infrastructure requires more robust tools (like Composite AI, which integrates different AI methodologies), governance, and understanding.
The rise of LLMs: more than just ChatGPT
While OpenAI’s ChatGPT is arguably the most popular large language model, it’s far from the only option. In 2024, we’re seeing a broad range of LLMs being adopted across industries, such as Google’s Gemini, Meta’s LLaMA, and Anthropic’s Claude. Each model brings its unique capabilities – Gemini, for example, is integrated to Google‘s into its web search, while Meta’s LLaMA is better optimized for research use.
Interestingly, businesses are using these models not just for customer service but also for tasks like marketing automation, data analysis, and even software development. Many organizations are transitioning from using off-the-shelf models to fine-tuning LLMs for more specific needs. According to the last Deloitte report, around half of the companies using AI in 2024 are leveraging pre-built models, but more are moving towards customized solutions to unlock more profound value from their data.
AI in action: adoption across industries
This year, businesses are pushing beyond basic AI chatbots. For instance, retailers are increasingly using AI for predictive analytics, personalizing customer experiences based on buying habits, while banks rely on AI to detect fraud or optimize trading strategies. However, the transition from pilot projects to full-scale deployment is still in progress. Deloitte reports that only about 25% of companies have successfully moved beyond initial pilot phases, as many are struggling with issues such as data governance, security, and the high cost of scaling.
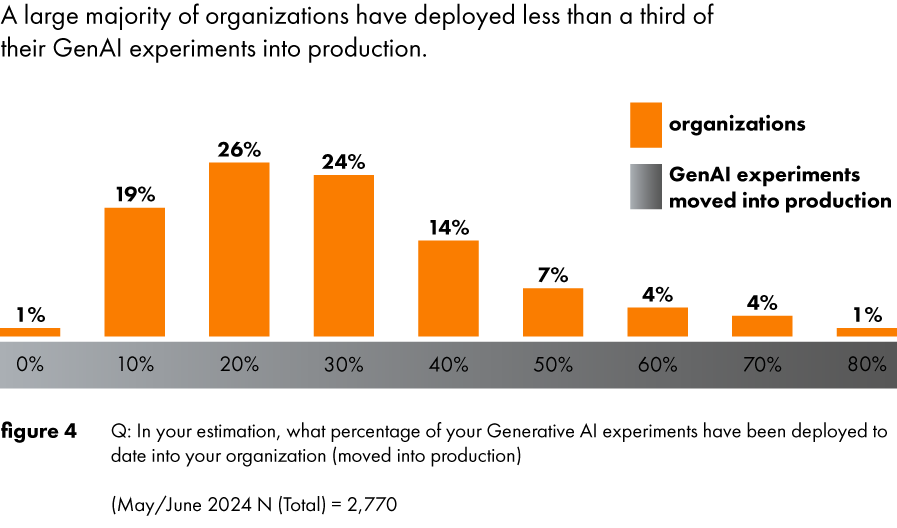
Source: Deloitte Q3 report
The impact of AI on IT infrastructure
One of the most significant side effects of AI adoption is its enormous demand for computing power. LLMs and other AI models, particularly those relying on deep learning, require vast amounts of energy and computational resources. Running these models efficiently necessitates high-performance hardware like GPUs and TPUs, and this has put unprecedented pressure on IT infrastructure.
We learned in Switzerland that AI-ready data and AI engineering are becoming essential for organizations looking to handle these demands at scale. AI engineering focuses on building sustainable frameworks for deploying AI, ensuring that businesses can scale without incurring technical debt. At the same time, AI-ready data is clean, structured, relevant, and complete data that has been processed to support practical artificial intelligence and machine learning applications.
Additionally, the rapid growth of AI has pushed companies towards hybrid cloud solutions that combine on-premise infrastructure with cloud computing. This approach allows for scalable resources that can be ramped up or down based on real-time demands, helping to manage AI’s intensive computational needs while keeping costs manageable.
The role of circular IT solutions in scaling AI
As AI continues to scale, the challenge isn’t just about having enough computational power—it’s about doing so efficiently and sustainably. This is where circular IT solutions come into play. Many companies are now integrating circular hardware into their data centers, allowing them to manage costs while meeting their growing demand for computing power.
Circular IT helps companies extend the life cycle of their infrastructure, reducing electronic waste while keeping costs in check. In 2024, with sustainability becoming a significant business driver, this approach is gaining traction as businesses look for ways to balance scalability and environmental impact. We are fully committed to this business model at Ynvolve and are happy to guide you with your first steps towards sustainable IT.
AI beyond the hype: challenges and opportunities
Despite the excitement surrounding AI, challenges remain. According to Gartner, businesses are starting to confront issues like AI governance, risk management, and data privacy concerns. Scaling AI isn’t just a technological challenge; it requires a structured approach to managing data, ensuring compliance, and navigating ethical issues.
Moreover, as AI moves beyond the “Peak of Inflated Expectations,” companies need to prepare for the “Trough of Disillusionment,” a phase where the limitations and difficulties of implementing AI come to the forefront. Many will realize that AI is not a one-size-fits-all solution and requires deep customization and a long-term strategy to achieve measurable success.
The road ahead: what does this mean for businesses?
In 2024, the state of AI is a mixed bag—there’s incredible potential, but companies need to navigate the challenges of scaling effectively. From the immense computing power demands to issues of governance and sustainability, AI adoption requires a strategic approach. This involves utilizing hybrid cloud models, integrating circular IT solutions, and continuously iterating on AI frameworks to keep up with evolving needs.
Ultimately, businesses that can align their infrastructure with their AI ambitions will be best positioned for success. As AI continues to evolve, so too will the landscape of IT infrastructure. Companies that can balance cutting-edge technology with scalable, sustainable solutions will be the ones leading the charge in the future of AI.
In a nutshell, while AI’s journey through the hype cycle is ongoing, its long-term value is undeniable. However, businesses must be prepared to invest in not only the technology but also the infrastructure needed to support it sustainably. Luckily for you, for all your sustainable infrastructure needs, we are always one click or phone call away, so don’t hesitate to reach out!




